Minto – Condition Monitoring
Condition monitoring involves tracking parameters, such as temperature or vibrations for each asset. The advent of the Internet of Things (IoT) brings the power of big data and machine-to-machine (M2M) communication to streamline the processes. This enables real-time monitoring of machines for better predictive analytics. In turn, it saves costs resulting from machine down-times and faulty production.
Minto is an Indian startup that develops a smart condition monitoring platform for rotating machines. The startup’s wireless, non-invasive device plugs into moving machines and collects high-resolution data to monitor them. The solution covers process manufacturing, utilities, and energy applications, as well as identifies faults before machines break down.
Ioticiti – Fleet Management
Fleet management solutions aim at minimizing machines’ mileage for the maximum profit and cost savings. M2M-based platforms connect vehicles in a fleet to automate dispatch and performance monitoring. Moreover, they transmit vehicular information in real-time, a feature that helps greatly in case of any accidents or failures for a fast response.
Canadian startup Ioticiti uses the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) to build a fleet management product. The startup’s solution equips vehicles with a M2M connectivity platform to map and manage unload wait-times and optimize product deliveries. The solutions can be applies in the construction, cold-chain, and waste management industries.
RoboticsX – Digital Factory
Most industrial processes require humans to operate or automate a single task at a time. Moreover, data generated from a machine generally stays within it. This leads to frequent downtimes, continuous delays, and redundant processes. M2M communication enables interoperability among machines and devices in smart factories.
RoboticsX is a German startup that develops machine-to-machine solutions to empower digital factories. X1 Grid, their manufacturing software platform, transfers data from connected industrial devices to enterprise resource planning (ERP) programs in real-time to increase the efficiency of the factory. The platform also assists engineers in reconfiguring devices without programming.
Elemental Machines – Lab Of The Future
Nowadays science-based industries encounter unique challenges in enterprise asset management. For instance, original equipment manufacturer (OEM) devices and testing tools do not share a lot of data that is crucial for important production decisions. M2M-based solutions automate data collection and optimize R&D activities in multiple industries, such as materials, life sciences, manufacturing, and energy.
The US-based startup Elemental Machines provides M2M solutions for technology-based industries. Their product, Element-D, collects metadata from OEM devices to provide actionable insights about workflows, machine health, and capacity utilization. The startup also provides solutions for monitoring ambient temperature and environmental conditions in manufacturing facilities and containers.
Weeve – Machine Economy
Machine economy involves networked and autonomous machines acting without the need for human intervention. It combines machine learning and M2M interactions to improve operational processes and attain higher production efficiency. This saves costs in hiring human labor needed to monitor systems for maintenance in Industry 4.0.
German startup Weeve offers solutions that bring the benefits of the machine-to-machine economy to the Internet of Things (IoT) devices. Their product, WeeveMQ, uses the patent-pending MQ Telemetry Transport (MQTTS) protocol for secure M2M, particularly for cases where battery life or computational resources pose a limitation. Additionally, the IoT Wallet, another product from Weeve, facilitates payments between connected IoT devices.
What About The Other 384 Solutions?
While we believe data is key to creating insights it can be easy to be overwhelmed by it. Our ambition is to create a comprehensive overview and provide actionable innovation intelligence so you can achieve your goals faster. The 5 machine-to-machine startups showcased above are promising examples out of 389 we analyzed for this article.
reposted from https://bit.ly/3dh3ysi
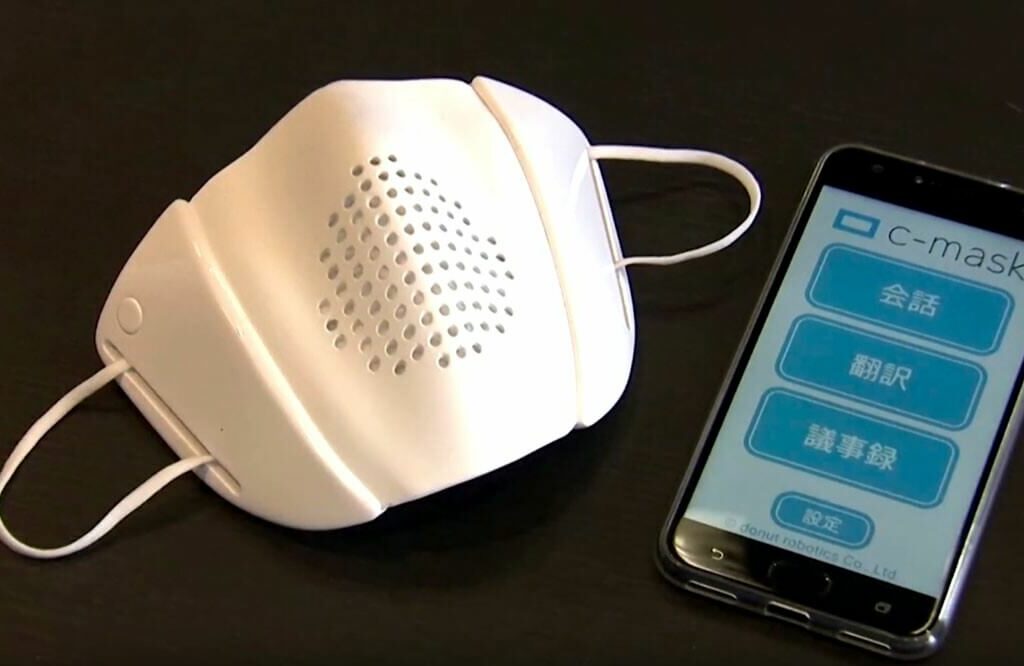





 What do you think when hearing about protective masks? Are you thinking that it keeps you safe? Maybe you feel a bit of reserved to live normally… Or they make you choke under the hot summer sun… However, in any case we should comply with the experts’ instructions! Undoubtedly, no one can claim that they provide you with comfort or it’s a humanlike habit…
What do you think when hearing about protective masks? Are you thinking that it keeps you safe? Maybe you feel a bit of reserved to live normally… Or they make you choke under the hot summer sun… However, in any case we should comply with the experts’ instructions! Undoubtedly, no one can claim that they provide you with comfort or it’s a humanlike habit…
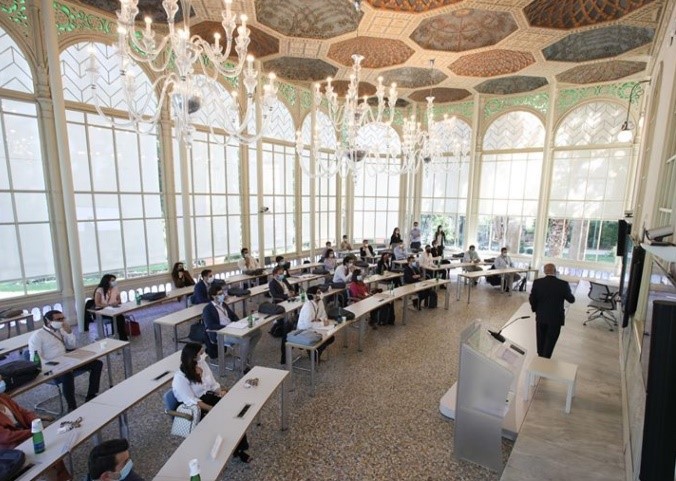

 Italy is preparing to make crucial decisions to revive the economy.
Italy is preparing to make crucial decisions to revive the economy.
 In Italy, more than half of the companies offered their employees online courses during the lockdown, with great satisfaction also for the workers who took part in it and who declared they preferred the e-learning methods to the traditional ones, for flexibility and convenience of avoiding travel.
In Italy, more than half of the companies offered their employees online courses during the lockdown, with great satisfaction also for the workers who took part in it and who declared they preferred the e-learning methods to the traditional ones, for flexibility and convenience of avoiding travel.
 One of the major concerns of the Fourth Industrial Revolution is that artificial intelligence and automation – robots – will eliminate jobs, both blue-collar and white-collar roles in various industries.
One of the major concerns of the Fourth Industrial Revolution is that artificial intelligence and automation – robots – will eliminate jobs, both blue-collar and white-collar roles in various industries.
 What could the long stop due to the crown-virus emergency mean for education?
What could the long stop due to the crown-virus emergency mean for education?
 The COVID-19 pandemic has suddenly transformed learning and teaching around the world. In the People’s Republic of China, for example, at least 260 million students from elementary school to high school enrolled in online platforms during the epidemic.
The COVID-19 pandemic has suddenly transformed learning and teaching around the world. In the People’s Republic of China, for example, at least 260 million students from elementary school to high school enrolled in online platforms during the epidemic.