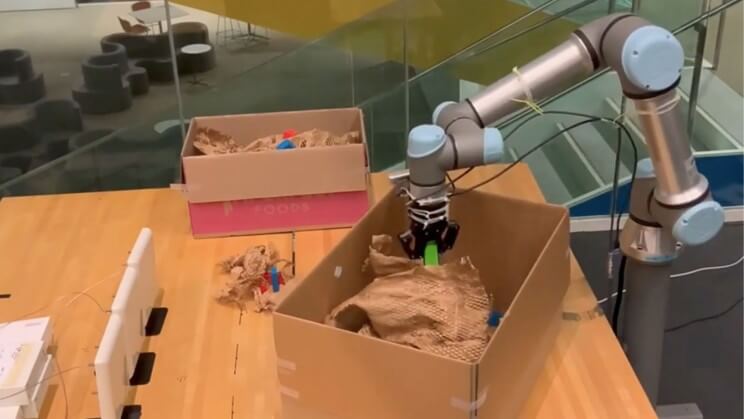
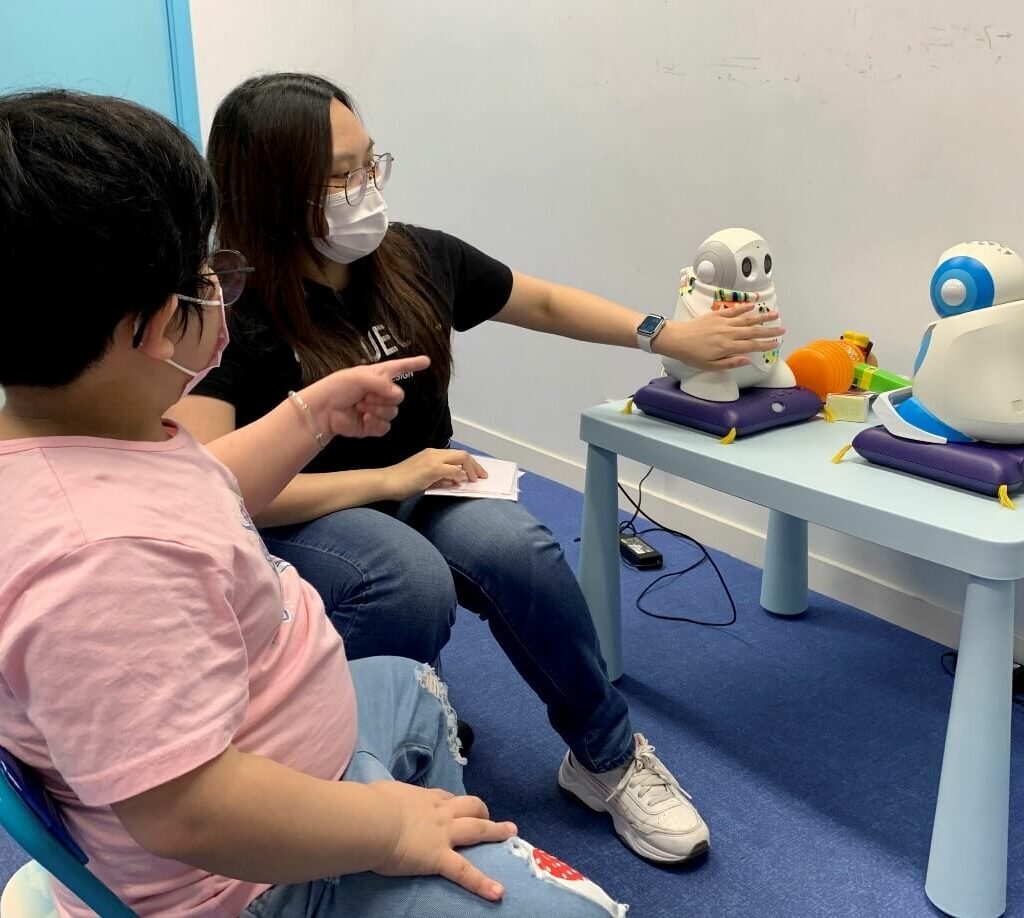
2020 was an important year in the green direction. Almost 560,000 companies in the industry and services have invested in green skills. A figure that translates into 39% of companies that asked at least half of the profiles sought to possess an aptitude for energy saving and environmental sustainability. 
For millions of companies, therefore, green expertise is considered necessary to carry out the vast majority of professions. Its degree of importance is considered “high”, says Unioncamere.
Among the professions for which green skills are in great demand, civil engineers stand out (skill required for 68.7% of hires), followed by electronics and telecommunications engineers (63.4%), construction site management technicians (62.7%), occupational safety technicians (54.5%) and energy and mechanical engineers (52.8%).
An attitude to energy saving and environmental sensitivity is an essential requirement for working in the company. Green skills are required from about 80% of graduates most of whom with a higher technical education diploma.
By examining the main sectors, Unioncamere data shows that the construction sector (82%), mechatronics (82.7%), tourism and catering (83.8%) are more sensitive to the double transition – ecological and technological. And advanced business support services (84.8%).
It is also evident that green occupations are characterized by higher demand for problem-solving, digital skills and the ability to manage innovative solutions, both computer and mathematical.
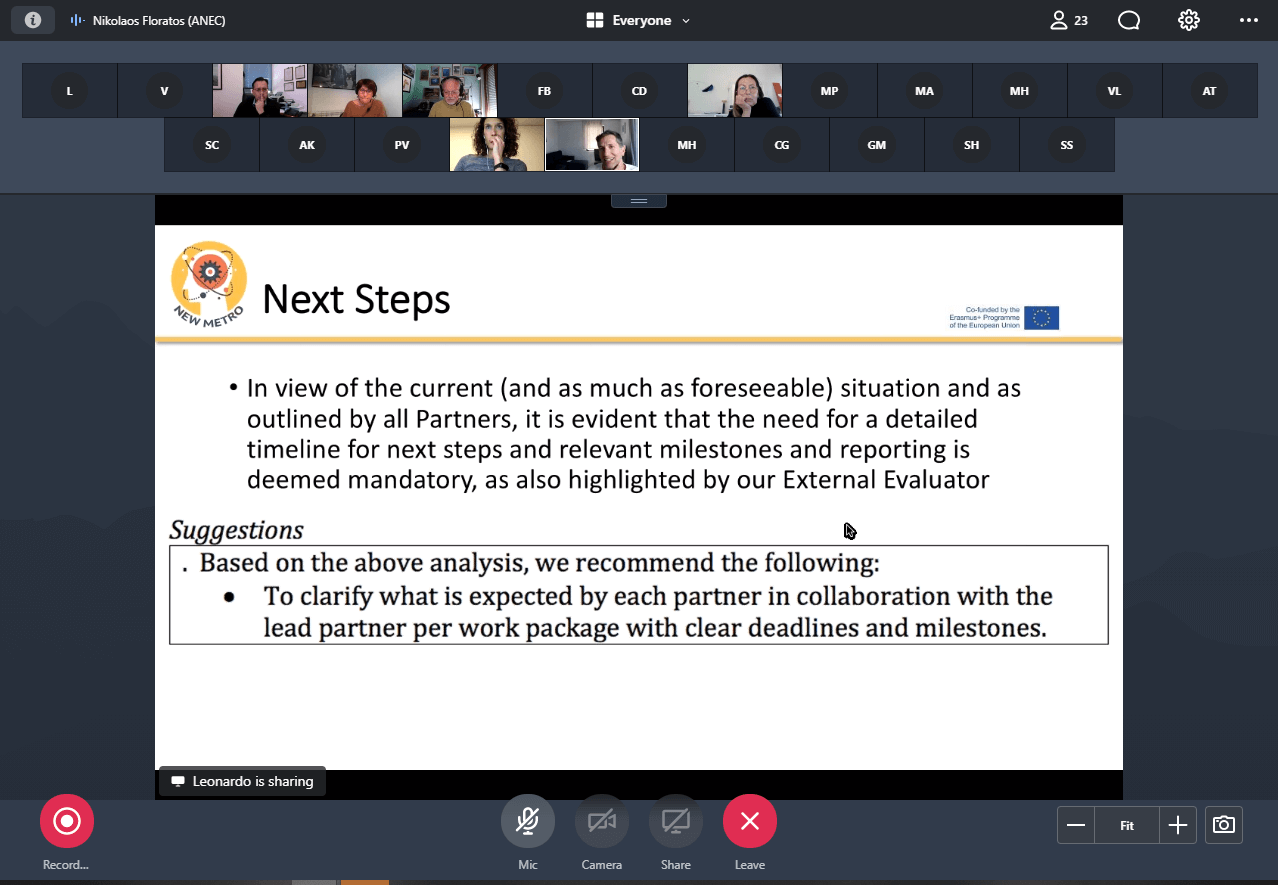
The analysis carried out by the New Metro Project Partners has identified as one of key competence the awareness of environmental issues. To this purpose further work is carried out within the Project to properly insert such capability in the curricula and educational path of students and workers.